Exploring Recent Advancements in Safety Certification Standards
In the fast-paced sectors of automotive, robotics, and aerospace industries, ensuring the safety and reliability of systems is paramount. Over recent years, standards such as ISO 26262 have undergone significant updates, reflecting technological advancements and industry needs. These evolutions, paired with global harmonization efforts and new guidance, critically impact how organizations approach compliance, risk management, and certification processes.
The Evolution of ISO 26262 and Related Frameworks
ISO 26262, titled "Road Vehicles – Functional Safety," is the cornerstone international standard for the functional safety of electrical and electronic systems in road vehicles. Originally published in 2011, the latest revision in 2018 expanded its scope from passenger cars to encompass all road vehicles except mopeds, aligning it more closely with the diversity of modern vehicle architectures.
This standard provides a comprehensive safety lifecycle, encompassing management, development, production, operation, and decommissioning. Notably, it introduces a risk-based classification system known as Automotive Safety Integrity Levels (ASILs), which systematically categorize hazards based on severity ( S0 to S3), exposure, and controllability.
Key Updates and Recent Developments
- Expanded Scope and Clarifications: The 2018 revision clarifies processes across hardware, software, and overall system development, emphasizing the importance of consistent safety requirements inheritance and risk assessment.
- Harmonization with Industry Trends: Efforts are ongoing to align ISO 26262 with standards in aerospace (like DO-178C) and robotics, promoting interoperability and reducing redundant compliance efforts.
- New Guidance on Software and Semiconductors: Parts 10 and 11 of ISO 26262 provide guidelines specific to software development and semiconductor integration, matching the increasing complexity of safety-critical systems.
- Focus on Change Management and Traceability: Emphasizing continuous traceability of safety requirements and rigorous change impact analysis, these updates help organizations respond promptly to design modifications.
Industry Trends and Harmonization in Safety Standards
Emerging trends in autonomous vehicles, collaborative robotics, and aerospace systems are pushing standards bodies to foster better synergy between different frameworks. For example:
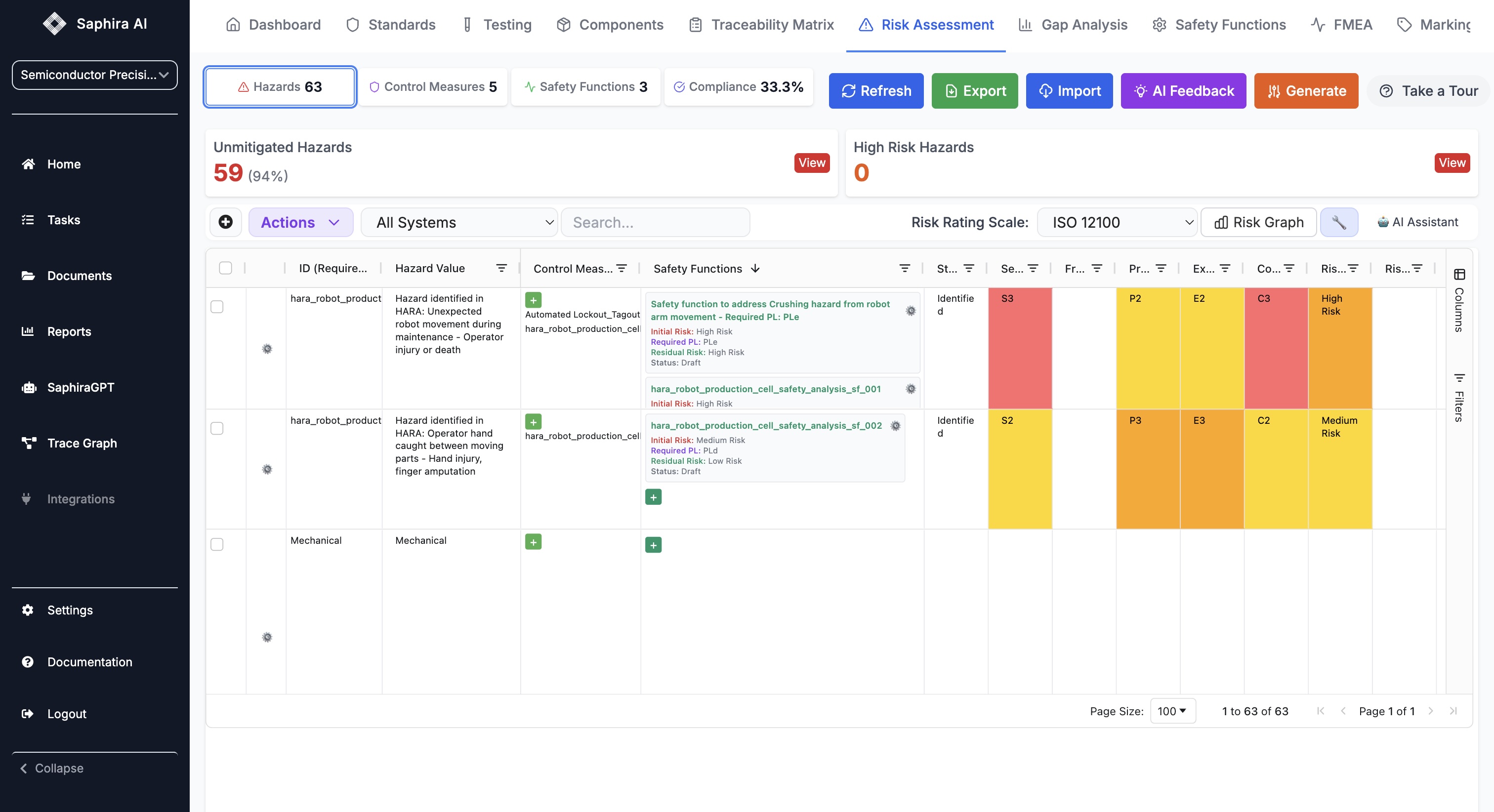
- AI-Driven Safety Assessments: The integration of AI tools, such as Saphira AI, automates the parsing of standards, requirement linkage, and safety documentation — dramatically reducing manual review time and human error.
- Global Standard Harmonization: Mutual recognition of safety assessments and certification frameworks is reducing barriers across regions, streamlining product deployment.
- Enhanced Industry Guidance: New supplemental guidance helps tailor standards like ISO 26262 to specific applications—such as semiconductors and software components—which are critical in modern systems.
Impact on Compliance Strategies
These advancements influence compliance strategies in several ways:
- Accelerated Certification Timelines: Automated safety assessments, document generation, and impact analysis streamline the certification process.
- Reduced Ambiguity and Gaps: Clearer classification of hazards and safety requirements, alongside automated traceability, improves confidence in compliance evidence.
- Proactive Change Management: Real-time change impact reports enable organizations to maintain safety integrity amid rapid development cycles.
Leveraging AI for Safety Innovation and Efficiency
Saphira AI exemplifies how AI-powered tools transform safety certification workflows by:
- Automating Standards Structuring: Converting directives and standards into actionable, traceable test and requirement lists.
- Retrieving and Citing Standards: Quickly accessing latest standards text and clauses, ensuring compliance alignment.
- Ensuring Continuous Traceability: Syncing test records and rework data automatically to maintain up-to-date compliance documentation.
- Performing Impact Analysis: Generating reports on the safety implications of design changes instantly.
This level of automation not only reduces manual effort but also mitigates risks of oversight, ensuring higher safety confidence in safety-critical applications.
Conclusion
The evolving landscape of safety certification standards reflects the rapid technological progress and increasing safety demands across automotive, robotics, and aerospace sectors. By keeping abreast of updates like those in ISO 26262 and employing advanced AI tools such as Saphira AI, organizations can streamline compliance workflows, accelerate certification timelines, and uphold trust in their safety-critical systems. Embracing these innovations is essential for maintaining industry leadership in a future where safety is ever more integral to technological advancement.
Author Note: As a contribution to Safety & Innovation Insights, this overview underscores the importance of integrating cutting-edge AI solutions with evolving standards to navigate the complex terrain of safety compliance successfully.